Integrate an Altinn app with Maskinporten
How to setup an integration between an Altinn App and Maskinporten.
This guide details how to set up an Altinn application to use the built-in Maskinporten authentication client (IMaskinportenClient) for making authorized requests on behalf of the app owner, as opposed to the active user.
In order to set this up, the following must be done:
- Ensure organization has access to Azure Key Vault.
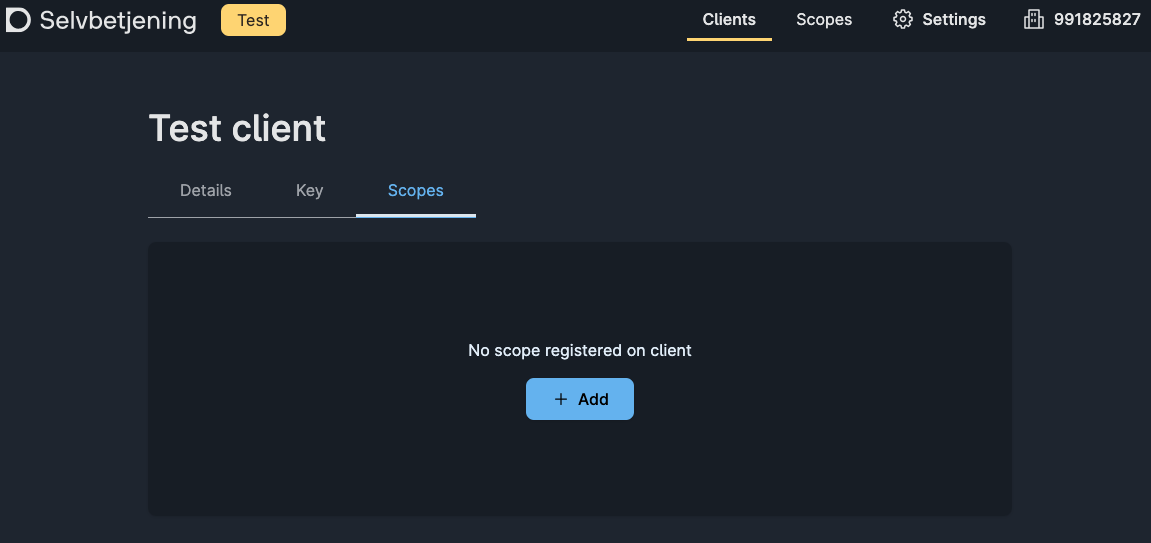
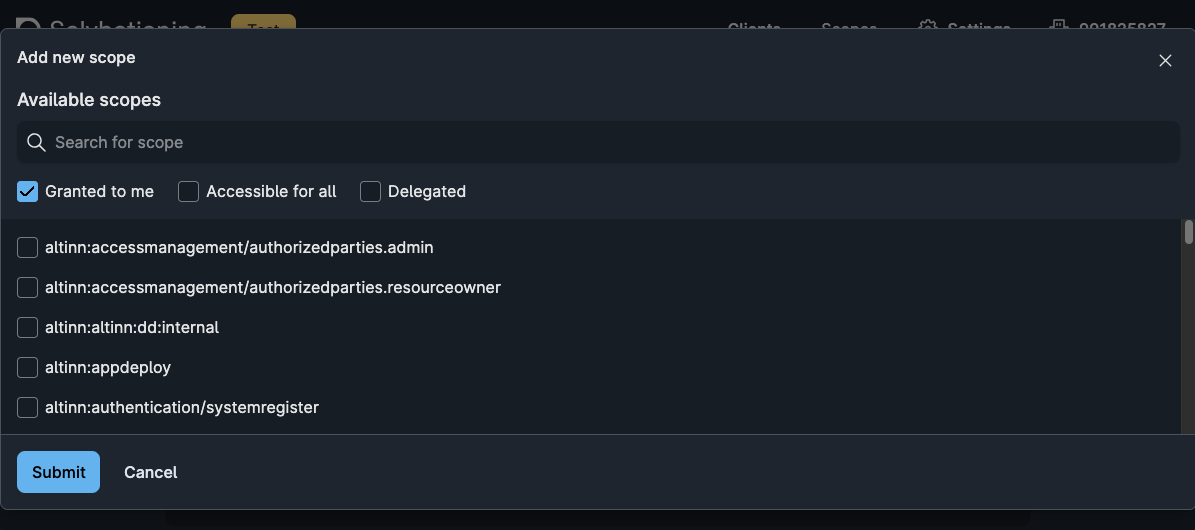
- Create a Maskinporten integration in the self service portal.
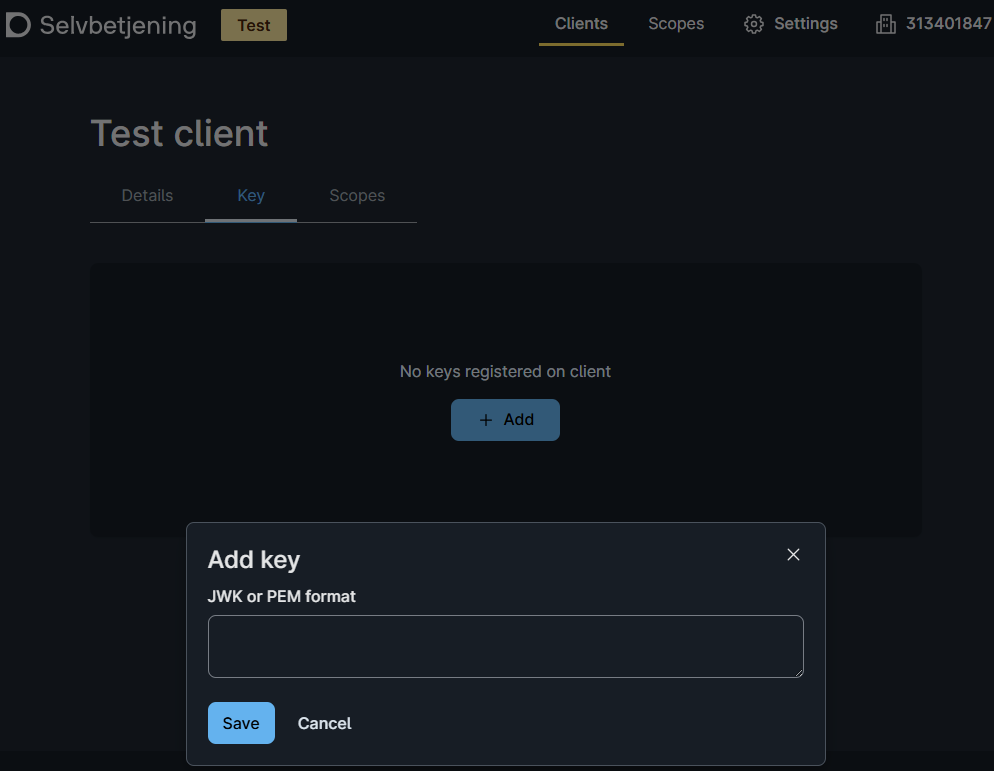
- Store the authentication key for the integration in Azure Key Vault.
- Set up the application to use the Maskinporten client and retrieve secrets from Azure Key Vault.
Azure Key Vault Access
Before proceeding with this guide, make sure you have access to Azure Key Vault for your organization. This ensures that the keys created further on in the guide can be stored properly as secrets in Azure.
If access is missing, please refer to Access to logs and secrets.
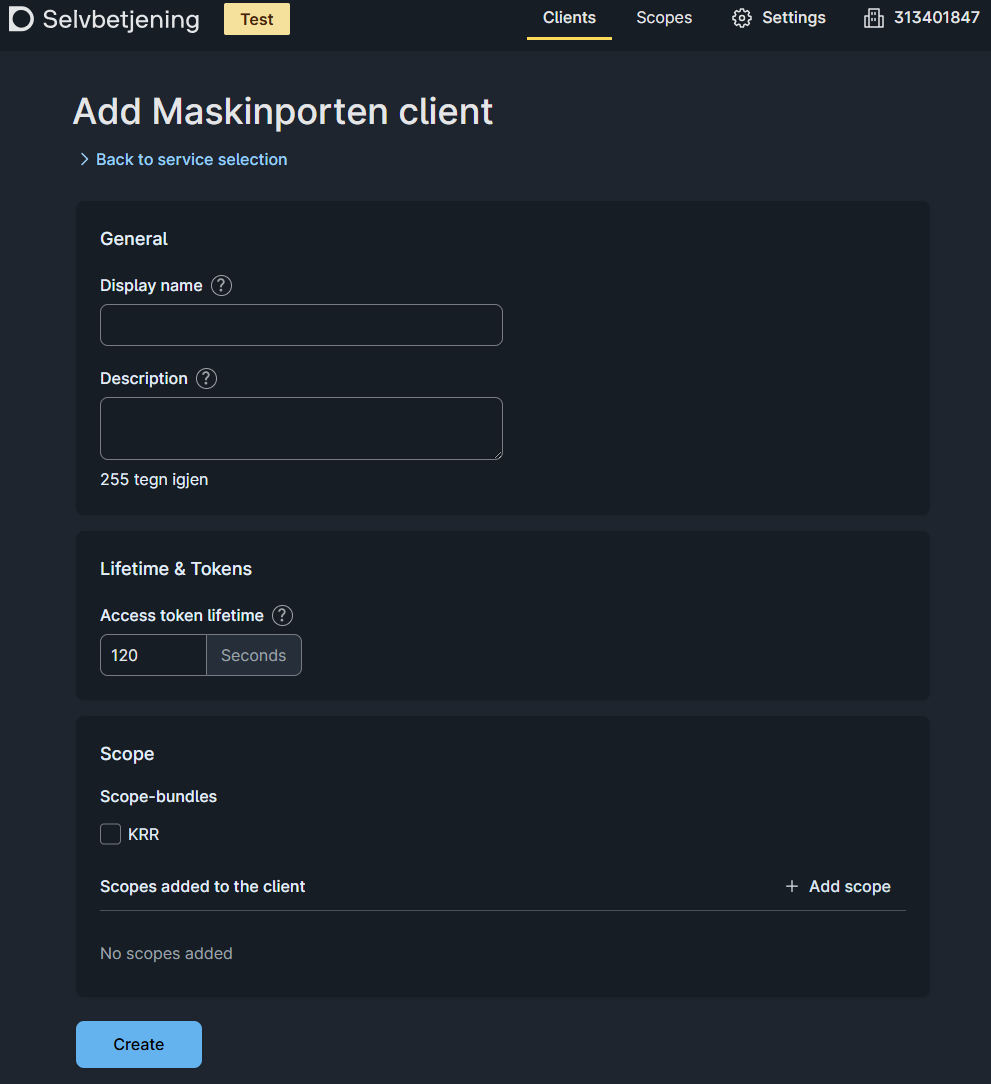
Maskinporten Integration
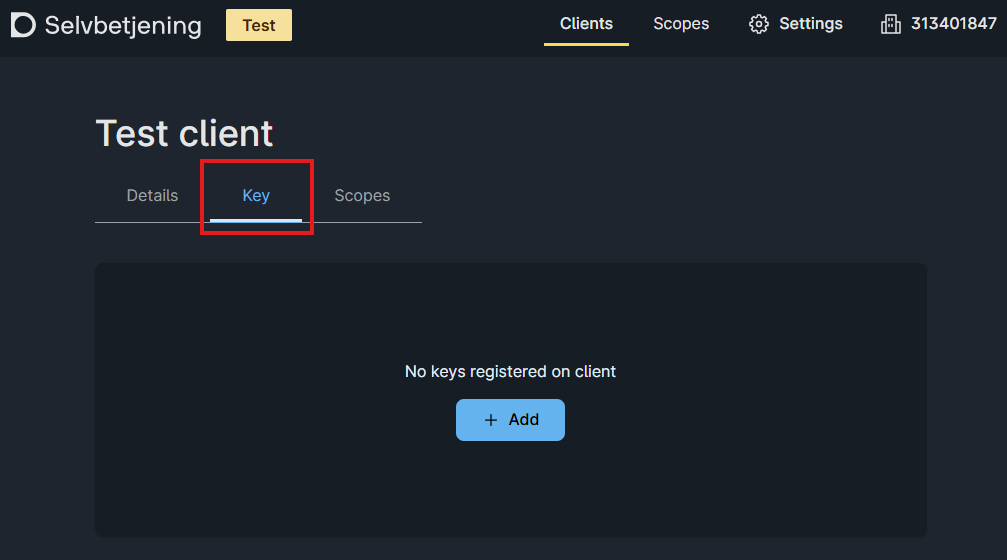
In this section we will set up the Maskinporten client. A part of setting up the client includes creating keys that should be stored in Azure Key Vault later on in the guide. If different people in the organization have access to different resources needed in this process, please cooperate and do the following steps on the same machine. This is recommended to avoid sending secrets between machines.
When access to creating secrets in Azure Key Vault is confirmed, please proceed to create the integration.
Azure Key Vault Configuration
When preparing the application to use secrets from Azure Key Vault, there are some steps that need to be done:
Add the secrets retrieved during the Maskinporten client configuration to Azure Key Vault:
- The base64 encoded JWT public and private key pair
- The client ID for the integration
It is important that the name of these secrets in Azure Key Vault corresponds with the name of the section in the appsettings file in the application repository. E.g. if your appsettings section for the Maskinporten integration section looks like this:
App/appsettings.json{ "MaskinportenSettings": { "Authority": "https://test.maskinporten.no/", "ClientId": "", "JwkBase64": "" } }The secrets in Azure Key Vault should have names like this:
MaskinportenSettings--Authority MaskinportenSettings--ClientId MaskinportenSettings--JwkBase64For the application to be able to read the secrets from Azure Key Vault, it needs to be configured to do so. See the secrets section to achieve this.
Add the appsettings section example from above into the
appsettings.{env}.jsonfile.
Note: The secrets are read by the application on launch so if you make changes after the application is deployed, you will need to redeploy the application for them to come into effect.
Application Setup
The application automatically includes the built-in IMaskinportenClient which can be injected into your services.
Configuration Paths
The client will automatically look for a Maskinporten configuration at the default path “MaskinportenSettings”. If you wish to use a different path, perhaps because you are deploying multiple apps and you need each one to carry different credentials, you can configure this via the ConfigureMaskinportenClient method.
App/Program.csvoid RegisterCustomAppServices(IServiceCollection services, IConfiguration config, IWebHostEnvironment env)
{
// ...
services.ConfigureMaskinportenClient(
"YourCustomMaskinportenSettingsPath"
);
}Authorizing Http Clients
Typed and named Http clients can be authorized with the available extension methods, as illustrated below.
App/Program.csvoid RegisterCustomAppServices(IServiceCollection services, IConfiguration config, IWebHostEnvironment env)
{
// ...
// For external APIs that require raw Maskinporten tokens
services.AddHttpClient<CustomClient1>().UseMaskinportenAuthorization("scope1", "scope2");
services.AddHttpClient("named-client1").UseMaskinportenAuthorization("scope1", "scope2");
// For Altinn APIs that require Altinn tokens (exchanges Maskinporten token)
services.AddHttpClient<CustomClient2>().UseMaskinportenAltinnAuthorization("scope1", "scope2");
services.AddHttpClient("named-client2").UseMaskinportenAltinnAuthorization("scope1", "scope2");
}Manual Usage
If you need to fetch a Maskinporten token manually, you can inject the IMaskinportenClient in your service and retrieve tokens with the GetAccessToken and GetAltinnExchangedToken methods.
public class Example(IMaskinportenClient maskinportenClient) : IProcessTaskEnd
{
public async Task End(string taskId, Instance instance)
{
var maskinportenToken = await maskinportenClient.GetAccessToken(["scope1", "scope2"]);
var altinnExchangedToken = await maskinportenClient.GetAltinnExchangedToken(["scope1", "scope2"]);
// Do something with the tokens...
}
}Key Vault Configuration
Lastly, we need to add the Azure Key Vault configuration provider to our host. This is done by adding the highlighted code after the ConfigureWebHostBuilder method.
App/Program.cs//...
ConfigureWebHostBuilder(IWebHostBuilder builder);
// Add Azure KV provider for TT02 & Prod environments
if (!builder.Environment.IsDevelopment())
{
builder.AddAzureKeyVaultAsConfigProvider();
}